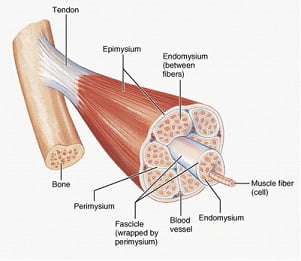
One lesser-known but valuable tool for multiple painful conditions is the low-level laser. The laser is a source of extremely pure, organized light, as opposed to something like a regular light bulb, which emits a scattered, disorganized light. We can liken organized light to the sound of a flute playing a single note, and disorganized light to the sound of a stone rolling around in a tin can. The laser is a non-painful treatment option that affects the local (near the area being treated) immune system, blood circulation, and the release of different chemicals that affect how we experience pain.
While it isn’t clear exactly how the laser helps a variety of painful conditions, there are two proposed means by which the laser improves pain:
- The light energy (called photons) is absorbed in the injured area and stimulates the production of Cytochrome C. Cytochrome C is a protein involved in cell metabolism and energy. When Cytochrome C is stimulated, it revs up the cell’s metabolism, and gives the cells more energy to heal the injured area.
- The light energy from the laser leads to the production of small amounts of singlet oxygen. Singlet oxygen is a reactive form of oxygen, which means that it is very easy for this type of oxygen to take part in chemical reactions. At high doses, singlet oxygen can be destructive, and has been used in cancer treatment to destroy cancerous cells. At very low doses, singlet oxygen can increase the number of cells. This may be one way the laser helps promote tissue repair.
The laser in a non-invasive, non-painful treatment option that can, in some cases, produce results immediately. For pain that has been around for a long time, more than one treatment session is usually needed for best results.