From 1991 to 2009, the number of prescriptions written for the strongest pain medications tripled. These medications are collectively named opioids and include morphine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone.Opioids are a type of pain drug that may cause serious side effects. From 2005 to 2009, the number of emergency room visits for nonmedical use of prescribed pain medication doubled. Therefore, the states and federal governments are acting to try to limit the amount of pain medication being prescribed.
At NMPI, we focus on finding the most effective treatment to relieve our patients’ pain – without surgery, steroid injections, or heavy painkillers. However, when a patient complains of severe pain and is not responding well to other pain medications, stronger, prescription opioids will be given.
 Some opioids, such as oxycodone, are often combined with Tylenol (acetaminophen) in one pill. Some examples of these combination drugs are Lorcet, Lortab, Norco, Vicodin (are all hydrocodone and acetaminophen), and Percocet (oxycodone and acetaminophen). Most often, severe pain is related to a condition that will improve over time. Ideally, all prescription pain medications should be given only while severe pain persists. Like any medication, there are risks and side effects:
Some opioids, such as oxycodone, are often combined with Tylenol (acetaminophen) in one pill. Some examples of these combination drugs are Lorcet, Lortab, Norco, Vicodin (are all hydrocodone and acetaminophen), and Percocet (oxycodone and acetaminophen). Most often, severe pain is related to a condition that will improve over time. Ideally, all prescription pain medications should be given only while severe pain persists. Like any medication, there are risks and side effects:
• Opioids can make you drowsy – which raises the risk of falling and severe injury
• Opioids when mixed with alcohol, anti-anxiety medication, seizure medication, muscle relaxants, or sleep-aids can be deadly.
• Opioids cause constipation and can lower sex drive.
• Patients can become physically and psychologically dependent on opioids.
• Overtime a patient with chronic pain can develop a tolerance for the opioid and need a higher dosage.
Keep in mind that not all pain requires such strong medication, and most patients with pain can be managed with drugs such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and aspirin-like drugs, called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as ibuprofen and Naproxen). When taken as directed, these less powerful drugs may be all that you need. (There are potential serious side effects with acetaminophen and NSAIDs, which I will discuss in a future blog.) For certain pains, some drugs are better than others. Sometimes we find that a drug we have been using may not actually be effective. A New York Times article on July 23, 2014 reported that for treating low back pain, acetaminophen was no better than a placebo.
Physicians have a responsibility to properly care for patients in pain. Some of these patients may appear to be at a higher risk to abuse opioids. Occasionally, patients complain of non-existent pain to obtain opioids for its mood-altering affect, called a “high.” The fact is that physicians who had been writing too many prescriptions for pain medication are now wary of prescribing any potentially habit-forming pain drugs. This has resulted in a decrease in emergency room visits for drug overdose and deaths from overdose, but it has also resulted in depriving many patients of medication they legitimately need to function normally.
At NMPI, when we treat patients in pain who have a history of drug abuse or who test positive on a written test to determine the risk of abuse, I believe that these two basic American traditions should be the guiding principles:
1. Innocent until proven guilty; and
2. In the words of Ronald Reagan, Trust but verify. Those patients who have problems or are at risk to not properly use pain medication need extra attention, not condemnation. They may be more difficult to treat, but that is why there are specialists to deal with complex pain problems.

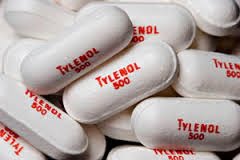



 Some opioids, such as oxycodone, are often combined with Tylenol (
Some opioids, such as oxycodone, are often combined with Tylenol ( nt of muscle pain was a routine part of the physical examination, time, money and suffering could be minimized. At the Norman Marcus Pain Institute,
nt of muscle pain was a routine part of the physical examination, time, money and suffering could be minimized. At the Norman Marcus Pain Institute, 
 I have a friend who has been complaining of weakness in his legs. He has a history of high cholesterol and has been on statins.
I have a friend who has been complaining of weakness in his legs. He has a history of high cholesterol and has been on statins.
